Electronic data communication or storage of any sort is inherently vulnerable to attack, particularly when wireless. Technical solutions are available, but if not implemented properly, they are worthless – just like using ‘pa55word’ as your password! Technicians and workshop managers/owners entrusted with customers’ data will need to follow all the relevant guidelines carefully to ensure:
- Systems are updated and secure
- Customer data is treated with respect and is secure
- Manufacturers guidance is always followed.
Vehicles
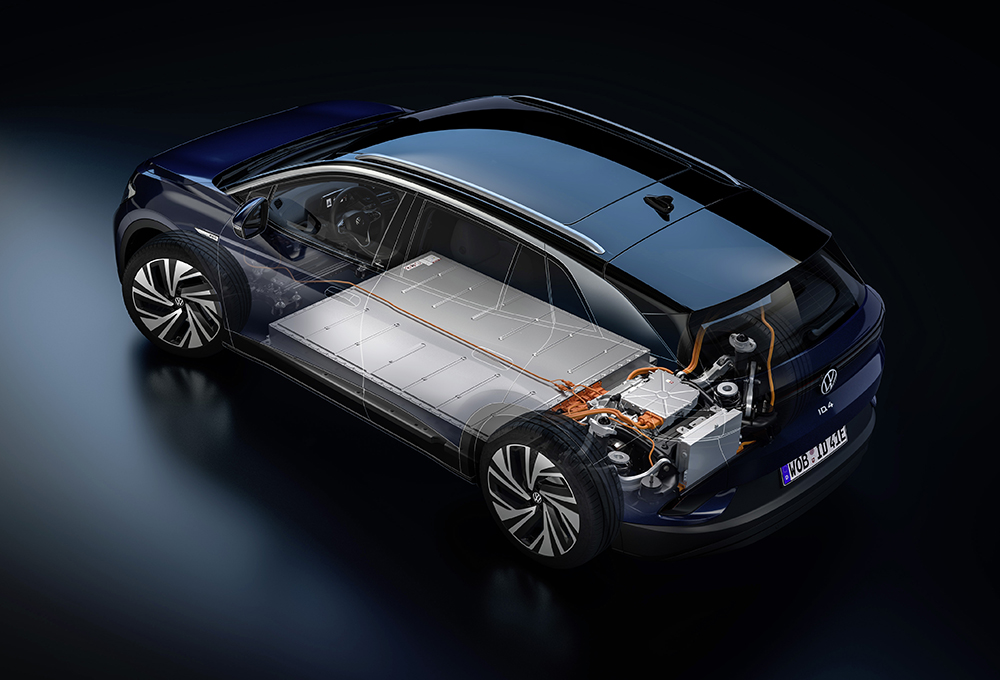
Connected cars will offer experiences similar to those on a mobile phone or a desktop voice assistant. Music on demand and social media are already available once the car and phone are connected. With these features integrated into the vehicle, manufacturers will unlock a new source of revenue, via streaming movies, for example.

Figure 6 Connectivity
Manufacturers and data access
There are two primary legislations that impact the availability of repair data:
- Competition law, specifically the motor vehicle block exemption regulation (MVBER), ensures fair treatment and equal access to tools, parts, and training for authorized repairers, main dealers, and independent workshops. The expiration of the “motor vehicle block exemption” is approaching in May 2023, and the government is currently in consultation regarding its potential replacement. Challenging non-compliance with competition law requires legal action.
- Vehicle type approval encompasses repair and maintenance regulations and includes technical requirements that can be used to assess non-compliance issues related to accessing technical information. If there is non-compliance, it can be contested through a vehicle type approval authority. Unlike competition law, which requires legal action, non-compliance with vehicle type approval can be challenged through the relevant authority.
Vehicle manufacturers are striving to exert more control over who can access vehicles and for what purposes, primarily due to concerns about cybersecurity. This control is being achieved through measures such as security gateways, and by July 2024, it will apply to all new cars. However, it is essential to maintain a competitive market that offers choices, ensuring that vehicle manufacturers do not utilize security certificates to control the aftermarket.
The introduction of certified coding and integration requirements for replacement parts has led to increased costs. Consequently, aftermarket parts, which are typically more affordable, have become more expensive. Additionally, the use of aftermarket parts may be restricted. While vehicle manufacturers have a responsibility to ensure the safety and security of their vehicles, using certificates to define rights and access limits can restrict repairs. Acquiring access to certificates often involves registering with the vehicle manufacturer, adding to the complexity. Simultaneously, there is growing pressure to exercise more control over the type-approval of replacement parts and the registration of independent workshops and technicians.
It is highly desirable that decisions regarding access to repair data be made and defined by legislators to prevent arbitrary restrictions imposed by vehicle manufacturers. By ensuring legislative involvement, the risk of unauthorized access being prevented through certificate restrictions can be minimized.
At the time of writing the legislation has not been agreed in the UK. However, significant representation has been made by UK AFCAR and others. The IMI recently stated in their response:
“Access to affordable and easily accessible technical information is essential for achieving this goal. Without such access, it can be overly expensive or burdensome to provide the necessary training to the skilled workforce required for the technology demands of modern vehicles. This could have the unintended consequence of reducing the number of SME repairers, who are critical to the provision of apprenticeship placements in the independent automotive aftermarket.”
Cyber essentials
Important reminder: The Cyber Essentials Scheme is a Government scheme that helps organisations to guard against the most common cyber threats from the internet and demonstrate commitment to cyber security. It covers five main technical controls which will protect companies against an estimated 80% of common internet threats. The controls are:
- Secure your Internet connection (Firewalls and routers)
- Secure your devices and software (Secure configuration)
- Control access to your data and services (Access control)
- Protect from viruses and other malware (Malware protection)
- Keep your devices and software up to date (Software updates)
Summary
Connectivity (for businesses and vehicles) is not just coming soon, it is already here. However, it is going to develop much further and has the potential to change the way we use and repair our vehicles. It could even change the way our vehicles use us!
The retained Motor Vehicle Block Exemption Regulation (MVBER) expires on 31 May 2023. This sets out automatic exemptions for certain categories of agreements related to the purchase, sale, and resale of spare parts for motor vehicles, and the provision of repair and maintenance services for motor vehicles. A similar regulation is expected to be in place soon.
The amount of data collected will be huge, and in huge data there is value. Indeed, it may become more of a profit line for vehicle manufacturers than the vehicles themselves, but we will have to wait and see. One thing is clear, the associated security risks will also be huge.