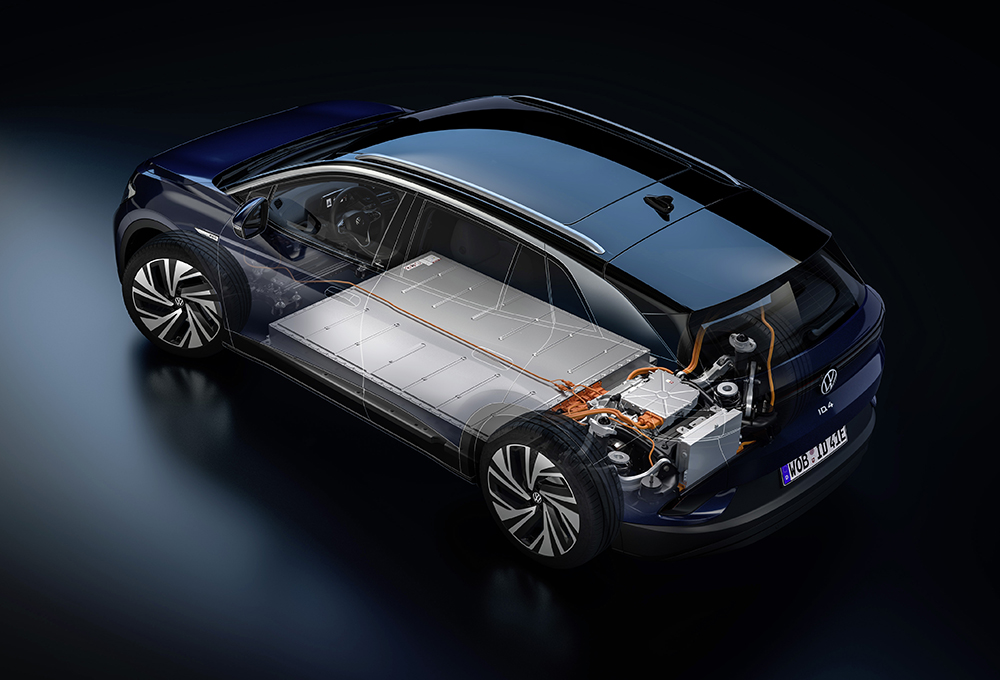
Location of charging ports
The charging port is where you plug in the cable that connects to the mains or to a dedicated charger. It may be under what looks like a fuel filler flap or in some cases behind the manufacturers’ badge.

Charging port (Source: Bosch Media)
Charging methods
There are essentially three ways to charge an EV:
- Trickle charge: This is the slowest method of charging your EV at home, using a standard 230V plug. It is only recommended when other options are unavailable
- AC charge: Having a wall box installed lets you charge 3-4 faster using AC domestic charging. AC public charging is also widely available.
- DC charge: This is the fastest way to charge an EV, but older EVs and PHEVs do not have this option. These public DC fast charging stations usually have power rated at 50kW and above. With this method, for example, you can top up a 60kWh battery from 20 to 80% in about 40 minutes. There are now also some ultra-fast charging stations that provide 150kW, and 350kWh chargers will become available in the future.
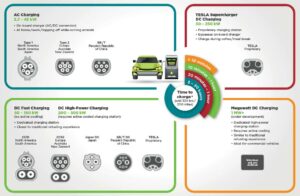
Time to recharge and cost
A typical recharge, particularly when travelling, is from 20% to 80% and may take 30 to 40 minutes. New and faster charging methods are starting to become available.
Exactly how long it takes to charge an EV depends on the type of vehicle, how discharged the battery is and the type of charge point used. Typically, pure-electric cars using standard charging will take about ten hours to charge fully and can be ‘opportunity charged’ whenever possible to keep the battery topped up.
Pure-EVs capable of using newer rapid charge points could be fully charged in around 30 minutes and can be topped up in around 20 minutes, depending on the type of charge point and available power.
The cost of charging an EV depends on the size of the battery and how much charge is left in the battery before charging. If you charge overnight, you may be able to take advantage of cheaper electricity rates when there is surplus energy. The cost of charging from public points will vary. It is also possible to register with supply companies who concentrate on energy from renewable sources.
Simple way to calculate cost of recharging:
- electricity is paid for in units (1 unit is 1kWh)
- charging is about 85% efficient (but often better)
To charge a large 100kWh battery from 20% to 80% is 60kWh
Divide this by the efficiency (85%) and the answer is just over 70kWh – multiply this by the cost per unit of electricity (let’s say 30p but this will vary) and it would cost about £21.
I currently buy electricity (overnight rate) at 7.5p per unit so a recharge like the above costs just over £5 or about £8 from fully discharged to fully charged. Not bad compared to the cost of a tank of petrol or diesel.

Charging (Source: Bosch Media)














