You will find the causes and remedies to the main problems related to tensioners, both for primary transmission (metal contamination and oxidation, broken central pin, broken stop contact, dents on the end stop), and auxiliary transmission (irregular opening of the aluminium case, metal contamination and oxidation, broken stop).
Timing Belt Automatic Tensioner

Metal Contamination and Oxidation
Causes:
- Contact with contaminating components: oil, dust, leakage of coolant
Actions:
- Remove leakage of coolant
- Remove leakage of oil and/or fuel
- Replace the faulty/damaged component
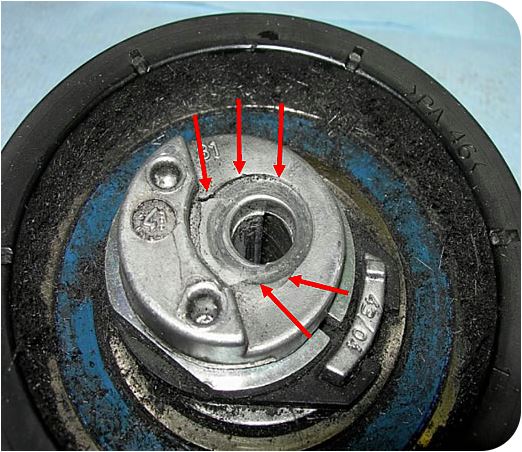

Broken Central Pin
Causes:
- Incorrect setting of the bolt: the torque applied is higher than the value specified on the maintenance sheet
Actions:
- Apply the correct tightening torque
- Use the torque wrench
- Replace the faulty/damaged component
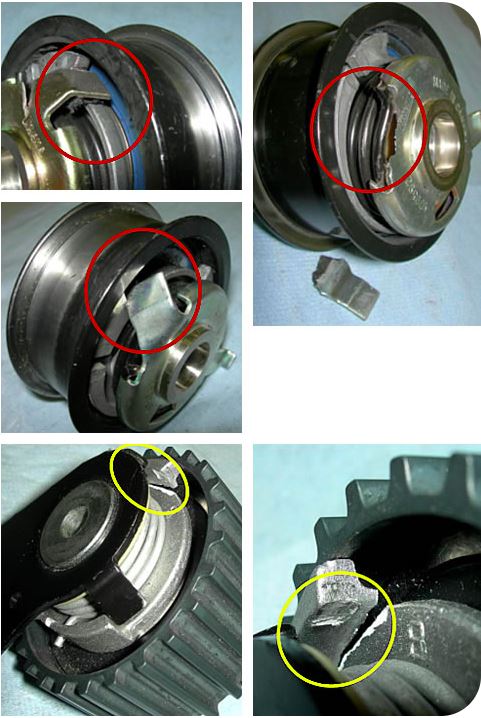

Broken Stop Contact
Causes:
- Incorrect setting of the tensioner: “excessive unload” condition with the belt excessively slack in the transmission
- Incorrect setting of the tensioner: “excessive load” condition with the belt tensioned in the transmission
Actions:
- Replace the components when the engine is cold
- Apply the correct tension to the belt
- Check the alignment of the reference indexes
- Check the belt tension after the adjustment turns
- Use the tensiometer to check the belt tension
- Replace the faulty/damaged component
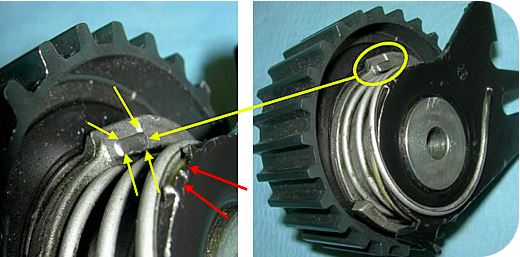
Broken Stop Contact / Dents on the End Stop
Causes:
- Incorrect setting of the tensioner with loss of capacity to modulate and compensate the belt tension variations
Actions:
- Replace the components when the engine is cold
- Apply the correct tension to the belt
- Check the alignment of the tensioner reference indexes
- Check the belt tension after the adjustment turns
- Replace the faulty/damaged component
Auxiliary Belt Automatic Tensioner

Irregular Opening of the Aluminium Case From the Loading Arm
Causes:
- High stress
- Load peaks from the belt
- Misalignment
- Binding of the component or other elements in the transmission
Actions:
- Use a belt with the correct length for the transmission
- Check the alignment between the pulleys
- Check the condition of the other components (damper and freewheel)
- Replace the faulty/damaged component

Metal Contamination and Oxidation
Causes:
- Contact with contaminating components: oil, dust, leakage of coolant
Actions:
- Remove leakage of coolant
- Remove leakage of oil and/or fuel
- Replace the faulty/damage component
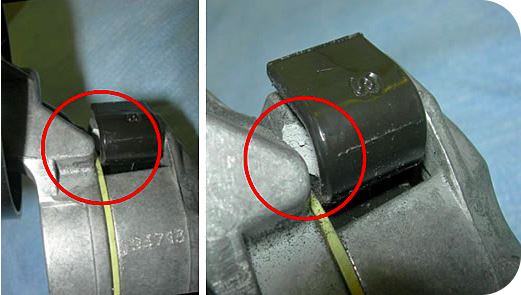
Broken Stop
Causes:
- Sharp blow due to accidental uncoupling during the installation and/or replacement stage
Actions:
- Replace using appropriate tools
- Replace the faulty/damaged component
info.uk@dayco.com